Interested in a versatile indoor plant? Hoya bella is an extraordinary hoya variety that thrives as an indoor plant. Allow gardening expert and plant enthusiast Madison Moulton to guide you through all aspects of this plant, including its upkeep and maintenance.
Characterized by fragrant flower clusters, Hoya bella is a charming cascading houseplant that requires minimal care, making it a perfect addition to any indoor garden. One of the most beloved species in the Hoya genus, it is cherished by hoya enthusiasts worldwide.
Embellished with lush green foliage, this hoya species remains visually appealing throughout the year, especially when adorned on a structure or hung from a basket or pot.
The allure of hoyas lies in their coveted blooms, a delightful sight only under optimal growing conditions. To ensure your hoya thrives and blooms, adhere to this comprehensive care guide.
Insight into Hoya Bella Plant
| Plant Type | Houseplant |
| Family | Apocynaceae |
| Genus | Hoya |
| Species | Hoya lanceolata subsp. bella |
| Native Area | Burma and northern India |
| Exposure | Bright indirect light |
| Height | 18” |
| Watering Requirements | Low |
| Pests and Diseases | Mealybugs, scale, etc. |
| Maintenance | Low |
| Soil Type | Well-draining houseplant mix |
| Bloom Color | White and pink |
About Hoya Bella
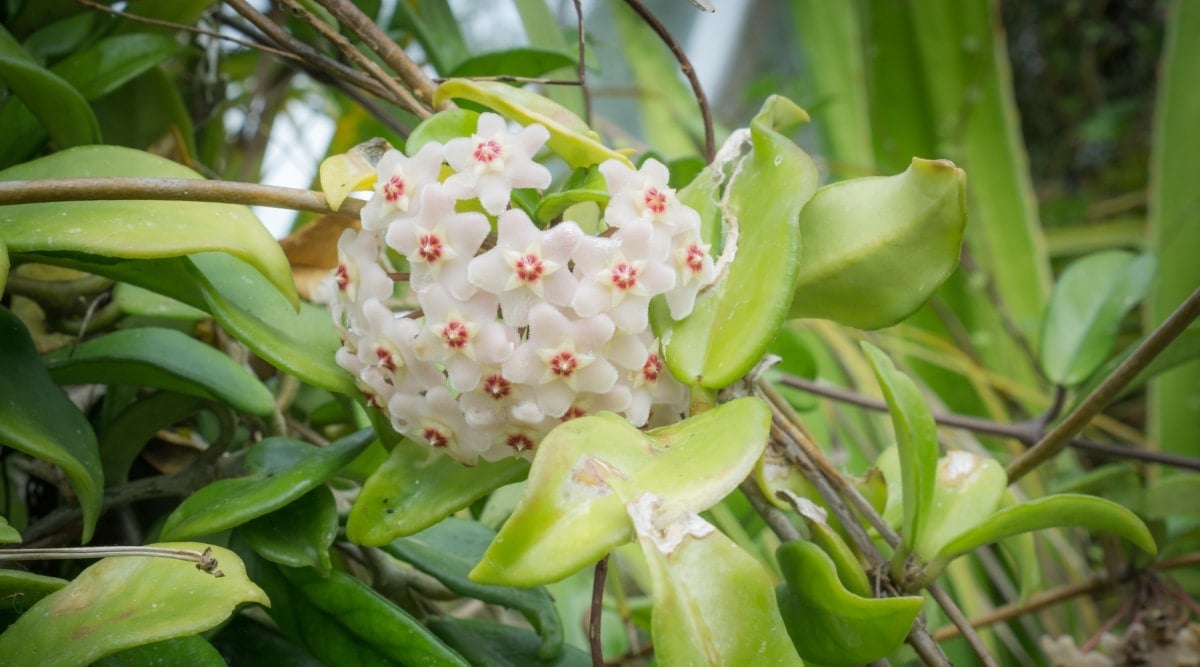

Hoya bella, an abbreviation of the full scientific name Hoya lanceolata subsp bella, is known for being a miniature version of Hoya lanceolata, commonly recognized as the Miniature Wax Plant or Miniature Wax Flower. Unlike its taller counterpart, the Hoya bella only grows to about 18 inches in height.
Named by botanist Robert Brown after his friend, Thomas Hoy, Hoya bella was given its specific epithet by William Jackson Hooker, an English botanist and the first director of Kew Gardens. Hooker, renowned for his botanical expertise, aptly chose ‘bella,’ meaning beautiful, to highlight this plant’s charm.
Hailing from northern Burma, Hoya bella thrives in warm, humid environments, explaining its preference for such conditions.
Characteristics
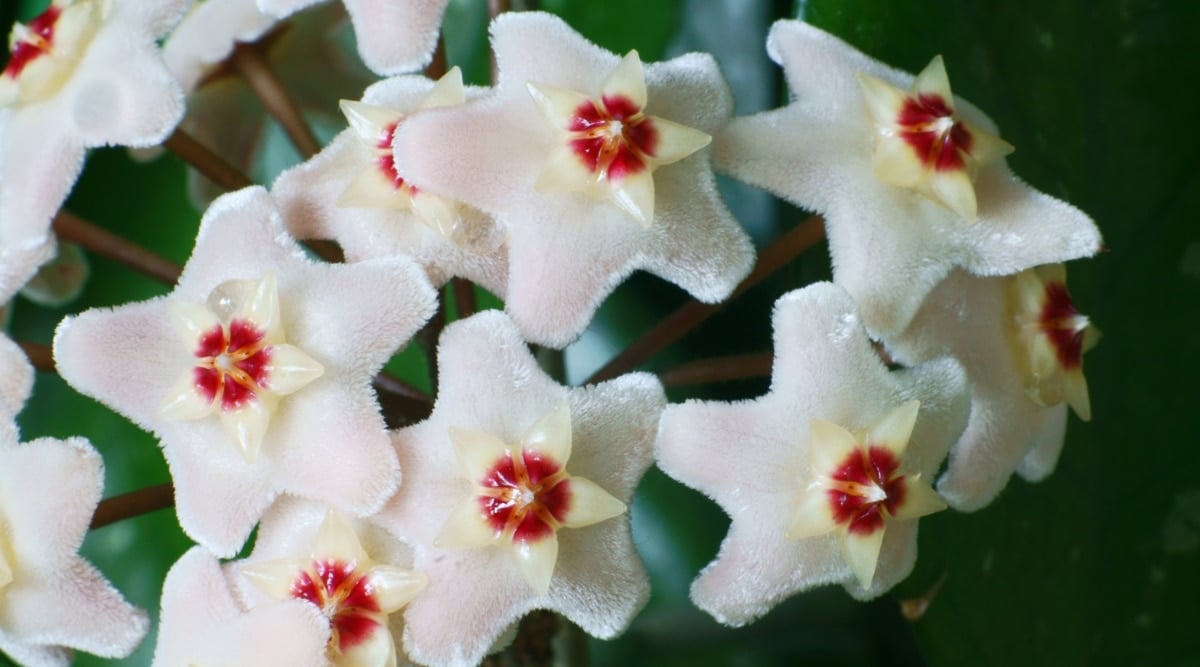

While outdoor growth is limited to USDA Zones 10 and above, Hoya bella thrives indoors or in a greenhouse in any climate. This epiphytic plant from tropical regions enjoys high humidity and features semi-succulent leaves that retain moisture, making it water-efficient.
This plant’s variegated varieties offer a tropical aesthetic, but its true allure lies in its star-shaped, fragrant white and pink flowers, which appear in clusters during summer. With a waxy texture, these blooms earned the plant its common name, Wax Plant.
In contrast to slow-growing hoyas, Hoya bella displays slightly faster growth and minimal maintenance requirements, making it ideal for novice hoya cultivators or those intimidated by more delicate species.
Propagation
While propagation of hoyas can be time-consuming due to their slow growth, the results are worth the wait.
Cuttings
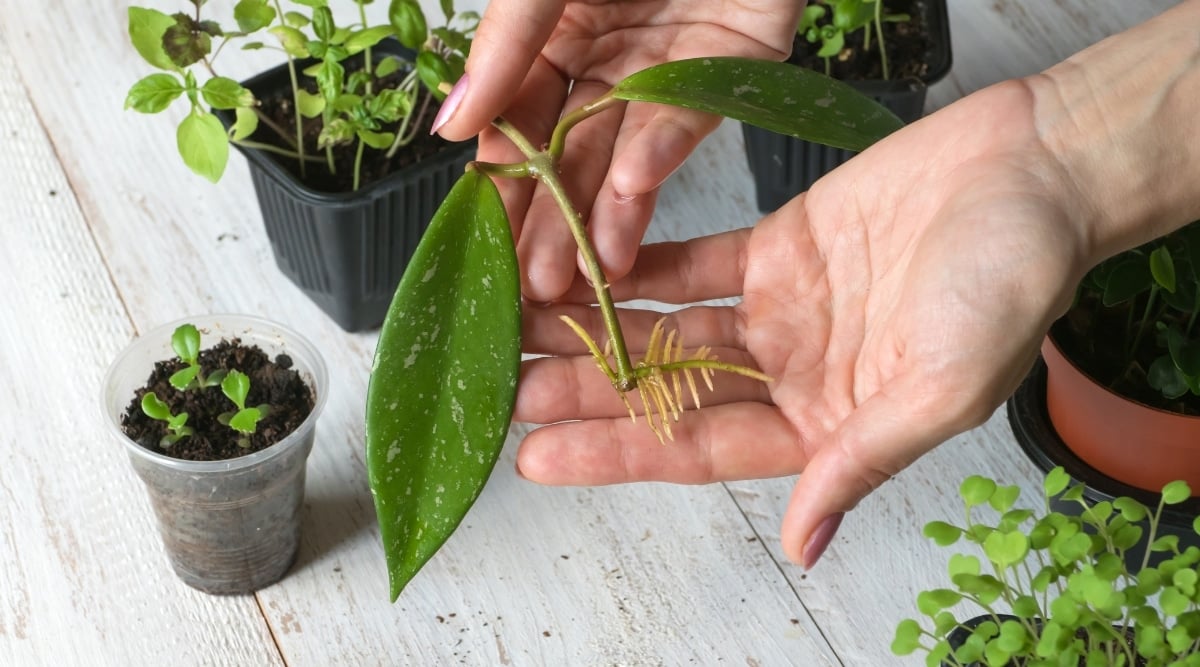


Layering
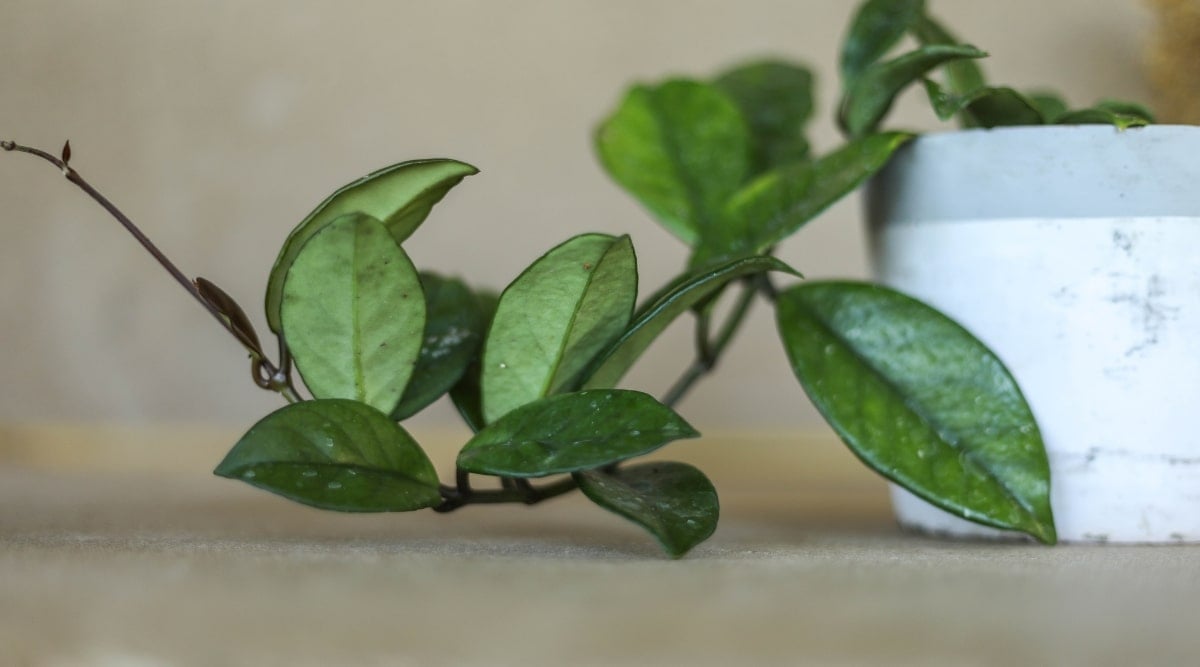


One of the most successful ways to propagate Hoya bella is by layering. This replicates how these plants spread naturally and allows them to root while still attached to the main plant, getting all the nutrients and moisture it needs.
Seed Sowing
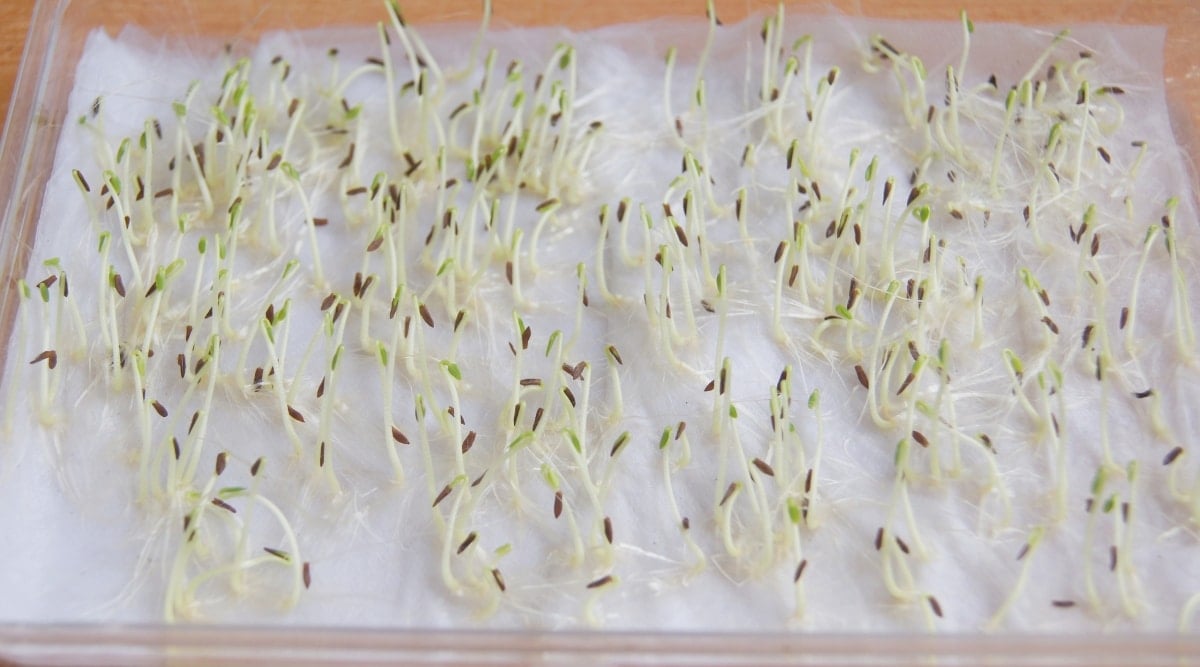


Seed is not the best way to propagate this plant due to low success rates compared to the other methods. But if you want to give it a go, plant the seeds in a seedling mix as you would with any other plant. Keep moist and place in a warm, well-lit area out of direct sunlight.
Repotting
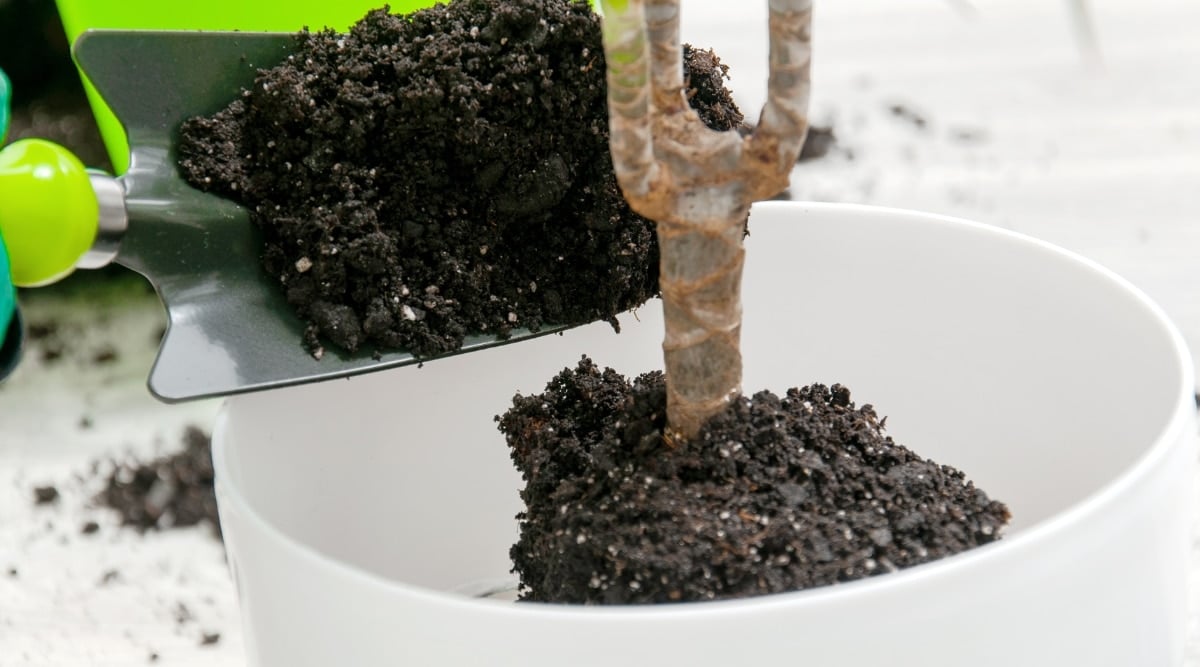


Repot your hoya every 2-3 years to replenish the soil and increase the pot size as it grows. It’s best to repot in spring so the plant gets enough time to settle in its new container before winter. Choose a container about 2
If you want your Hoya bella to thrive and blossom properly, it’s crucial to choose a pot that is a few inches larger to allow for growth in the upcoming years. Be cautious not to select a pot that is too big, as this can lead to flowering problems.
Prior to transplanting, prepare the day before by ensuring the plant is well-watered to prevent shock during the moving process. Set up the new container with a blend of potting soil and suitable drainage materials such as vermiculite, perlite, or clean sand mixed thoroughly. Delicately transfer the plant from its current container, minimizing root disturbance while eliminating as much old soil as feasible.
Employ a gentle touch and invest the time to execute the transplant correctly for optimal outcomes. Plant the Hoya bella in the new pot with the designated soil mixture and water adequately. If you plan on training the vines, consider installing supports accordingly.
How to Cultivate the Hoya Bella
Lighting Requirements
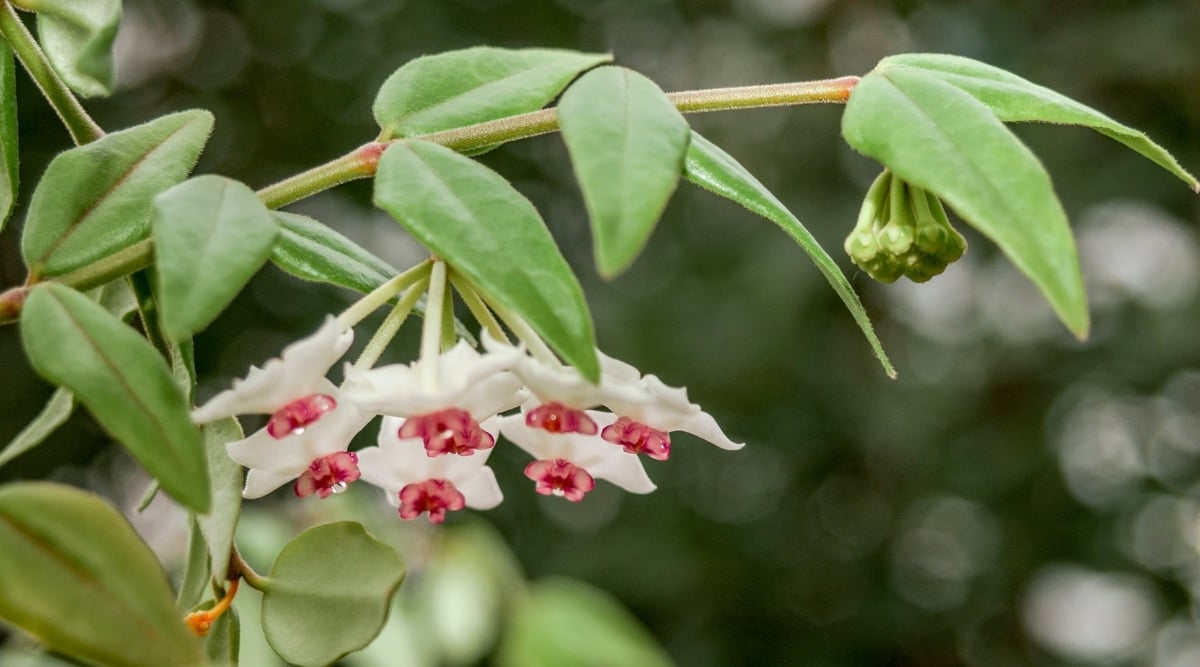

The Hoya bella plant thrives best in bright indirect or filtered light, necessitating a full day of exposure to such light to flourish. Insufficient light may impede growth and hinder flower production.
Flowering is directly influenced by the amount of sunlight the plant receives. Enhanced light exposure leads to better flowering results. In low-light settings, the stems may elongate, and any new leaves that sprout are likely to be small and stunted. Once flowering begins, it’s advisable to cease rotating the pot and minimize any unnecessary movement.
Ensure the plant’s leaves are safeguarded from direct sunlight, particularly during the intense summer months. If additional light is required, an hour of gentle morning sunlight can be beneficial. While east-facing windows are preferable, the Hoya bella can also thrive in locations with filtered sunlight from south or west-facing windows.
Watering Guidelines
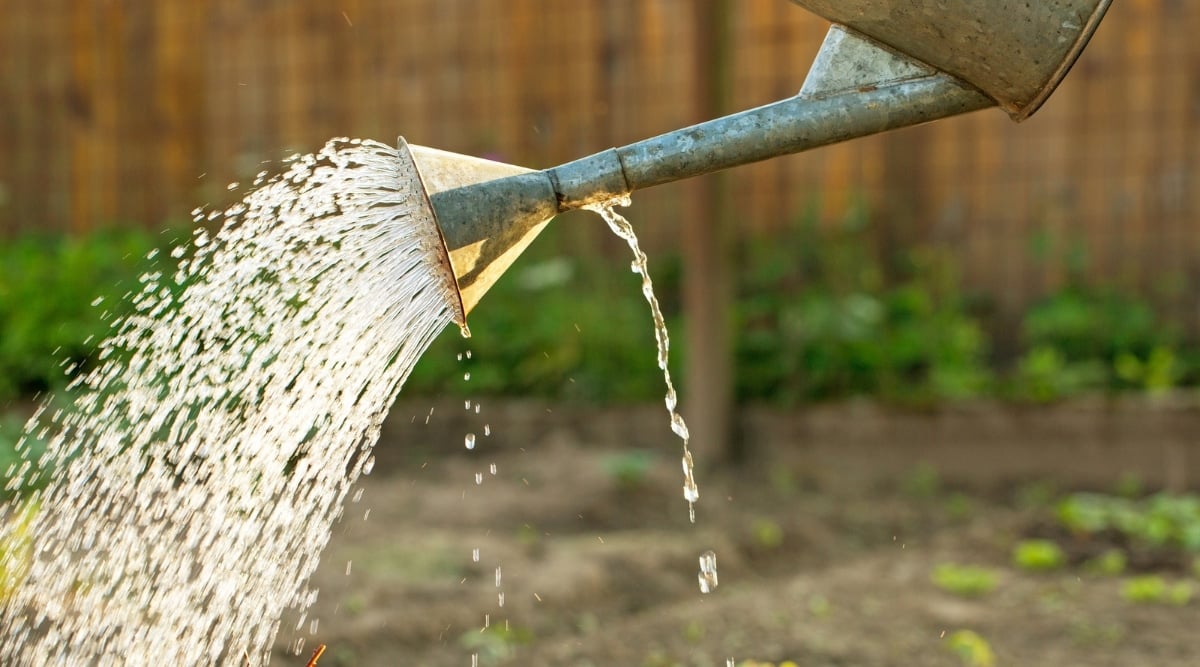

The succulent nature of the Hoya bella’s thick leaves provides insight into its watering requirements. As the leaves retain water to survive dry periods, this plant doesn’t necessitate frequent watering like other houseplants. However, overwatering should be avoided as these plants are sensitive to excess moisture and detest being in waterlogged soil.
Throughout the growing season, water the plant consistently but moderately. Allow the soil surface to almost dry out completely before the next watering cycle. Check the top layer with your finger and water when around half of the pot has dried. Additionally, lifting the pot to assess its weight can help gauge the soil’s moisture content, as damp soil will increase the pot’s weight.
Avoid watering when the soil is still damp, as excessive moisture can lead to fungal issues and ultimately root rot. Reduce watering frequency during the winter months when evaporation rates are lower and the plant’s water intake decreases.
Soil Composition
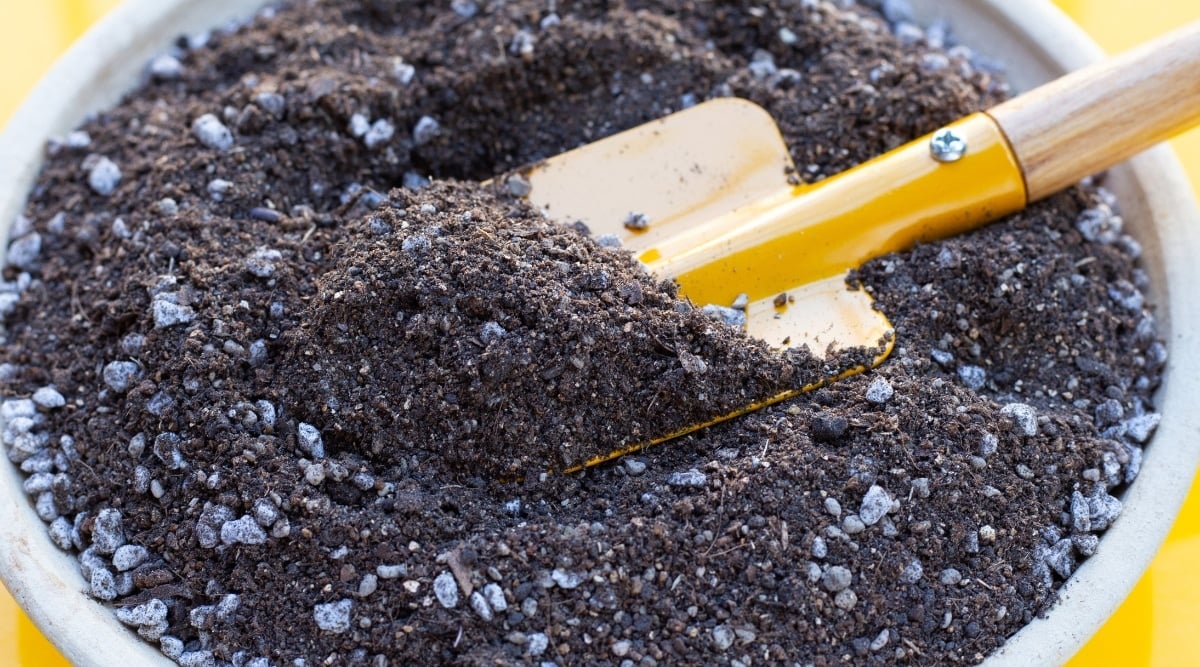

An airy, well-draining houseplant potting mix serves as the perfect soil blend for the Hoya bella. It can be potted in hanging baskets to cascade or trained to climb on a trellis or moss pole.
If a houseplant potting mix isn’t available, enhance regular potting soil with bark chips and perlite to boost drainage. As epiphytic plants, Hoyas can flourish with minimal soil, emphasizing the importance of excellent drainage for enhanced airflow. Moreover, ensure the container possesses adequate drainage holes to facilitate water runoff, as insufficient drainage can compromise soil aeration.
Temperature and Atmospheric Moisture
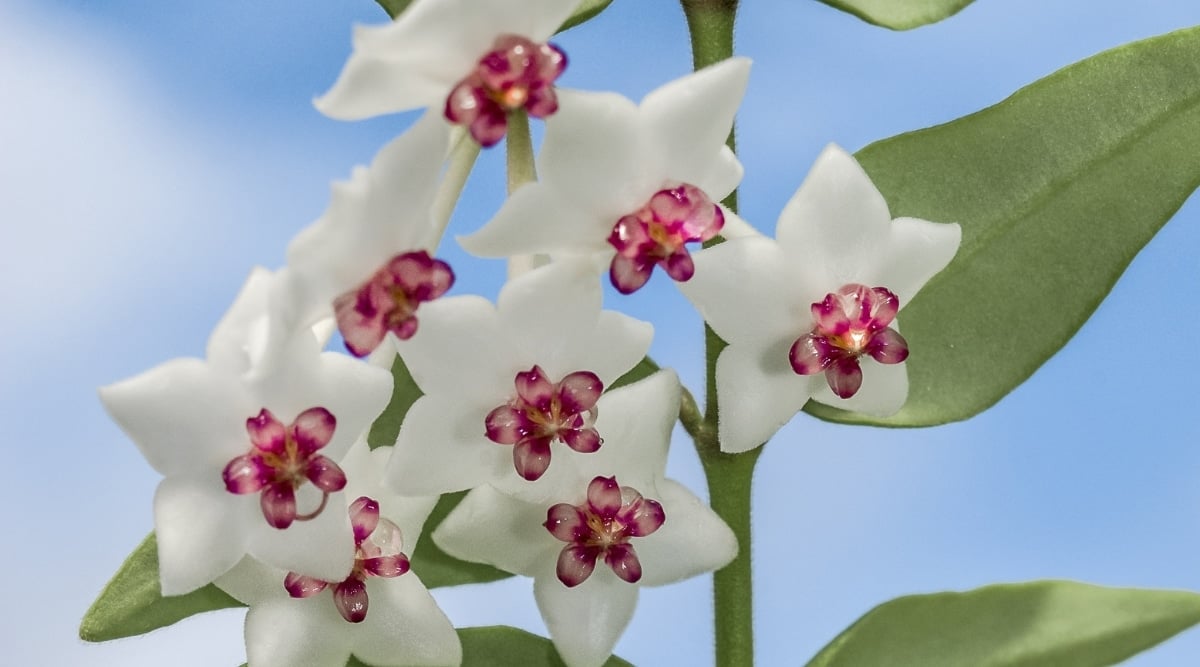

Favorable Conditions for Hoyas
For optimal growth, keep your Hoyas in humid environments with humidity levels over 50%. These plants can manage with slightly lower humidity levels due to their waxy leaves. While they can thrive in general household humidity, it’s best to avoid drafty areas that can negatively impact their growth. Hoyas prefer temperatures ranging between 75F and 85F and should be moved away from cold windows or doorways during colder months to prevent leaf damage.
Proper Fertilization Techniques
Feeding your Hoya bella with a nitrogen-rich fertilizer every few weeks during the growing season is essential. Use specialized plant food to support flowering. In the spring, nitrogen-based fertilizers encourage robust foliage growth. When approaching the flowering period, switch to a phosphorus-rich fertilizer to enhance the color and form of the flowers. Avoid fertilizing in winter when growth slows down, as new foliage is more susceptible to cold damage.
Effective Plant Maintenance
To maintain your Hoya’s shape, avoid removing flower stalks post-flowering, as new flowers will blossom on these old spurs. Light pruning is recommended to regulate growth and remove damaged or dead leaves. Pruning back long stems can stimulate branching, resulting in fuller growth and a healthier plant overall.
Addressing Common Issues
Avoid overwatering your Hoya to prevent root rot, which can be identified by wilting or yellowing leaves. Compacted soil can exacerbate this issue. If root rot occurs, trim infected roots with clean shears, replant in fresh soil, adjust your watering routine, and give the plant time to recover. Conversely, if your Hoya exhibits wrinkled, dried-out leaves, it might indicate underwatering. Ensure the soil is dry to the first few inches before watering again. Stunted growth could result from environmental stress or inadequate care, so monitor your plant closely to address any issues promptly.


Experiencing a pause in growth with your hoya plant beyond its winter dormancy phase could result from various factors.
One crucial factor to assess is the lighting levels. Hoyas require full-day bright indirect light to thrive optimally. Diminished photosynthesis can lead to slowed plant growth. Consider supplementing with grow lights or fluorescent lamps to enhance lighting if needed.
Inadequate nutrients can also hinder growth, so applying a nitrogen-rich liquid fertilizer can aid in fostering healthy leaves and robust growth.
Leaf Loss


Hoyas typically shed some leaves in winter due to temperature changes like cold drafts. Relocating the plant to a warmer spot and boosting humidity levels can prevent further leaf shedding, preserving the foliage for the forthcoming season.
Lack of Blooms
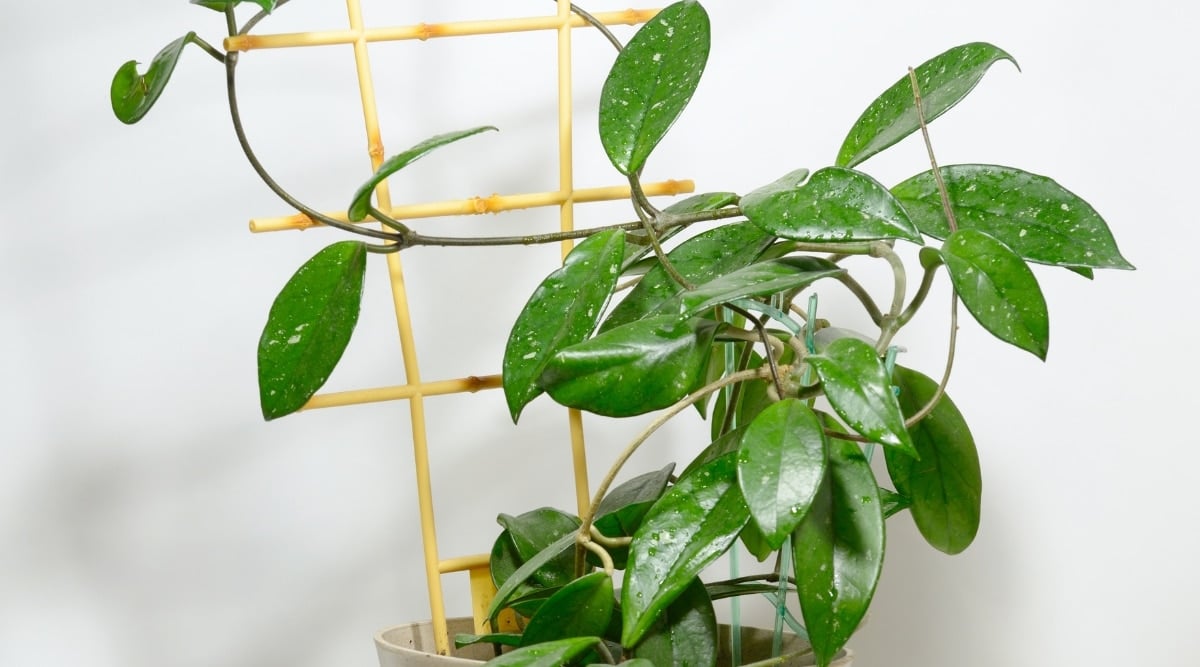


Younger hoyas require time to bloom, usually not flowering until they mature. For mature plants not flowering, ensure they receive adequate sunlight.
Additionally, evaluate the pot size, as overly large pots, excessive watering, or fertilization may hinder blooming.
Pests and Diseases
While generally resilient to pests and diseases, hoyas can be affected by specific issues:
Mealybug Infestation
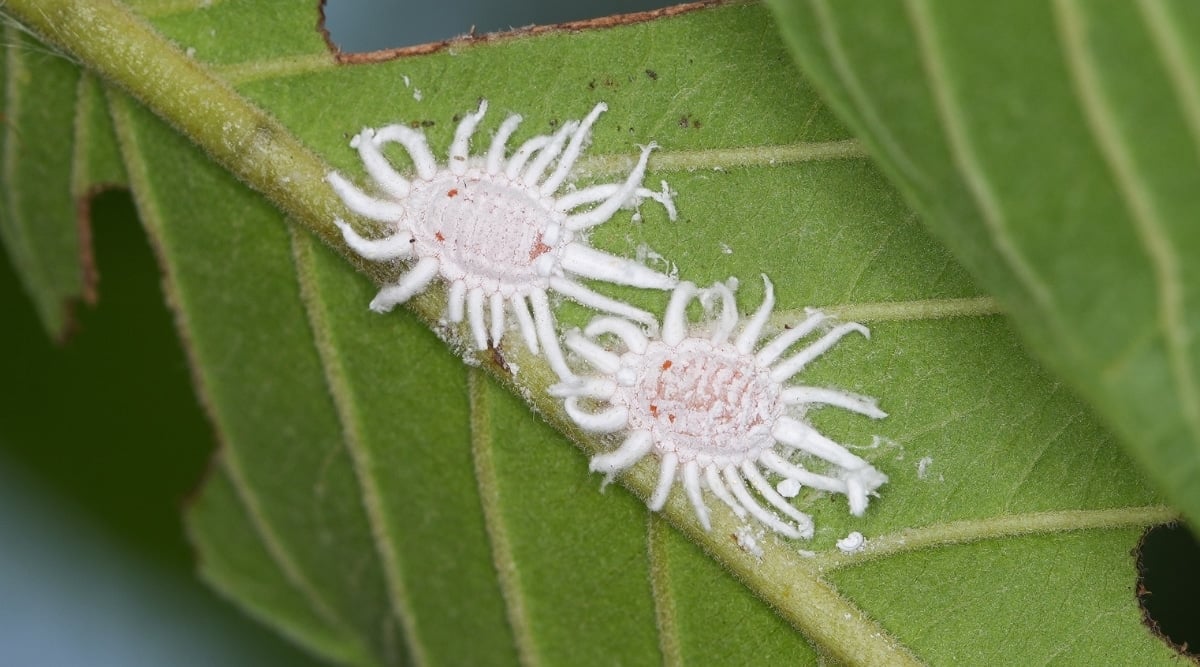


Mealybugs, common sap-sucking insects, can weaken hoyas by extracting sap from their leaves, leading to structural damage and sooty mold growth due to their honeydew secretions. Warm conditions favor mealybug infestations, making indoor plants vulnerable year-round.
These pests can hitch a ride on new plants, so inspect any acquisitions closely. Isolate and treat affected hoyas with insecticidal soap to eliminate infestations.
If only a few mealybugs are visible, use a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol to dislodge them before treating the plant with insecticidal soap to eradicate hidden eggs. Repeat treatments to ensure complete removal before reintegrating the plant.
Scale Infestation
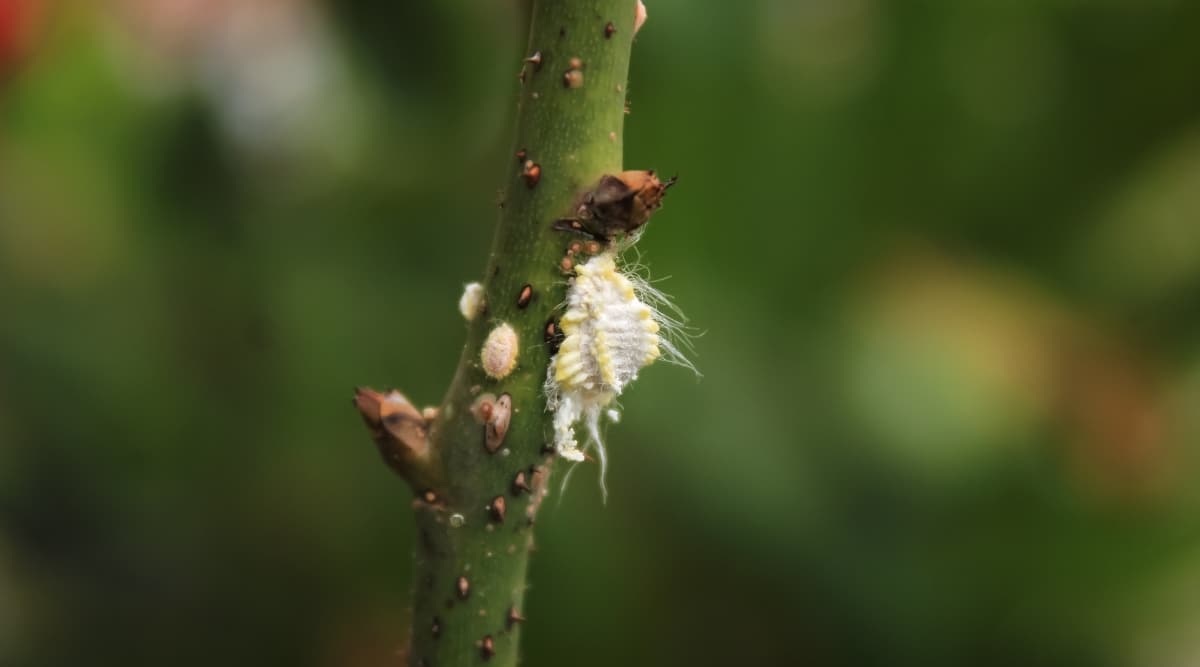


Scale, a larger category of sucking insects, can weaken Hoya bella by attaching to leaves and stems, noticeable through brown-to-beige bumps adhering to the plant.
To combat scale infestations, utilize insecticidal soap with multiple applications to address the issue thoroughly. Treat individual adult scale using rubbing alcohol on a cotton swab. It is advisable to isolate infected plants from others until the infestation is resolved.
Spider Mites
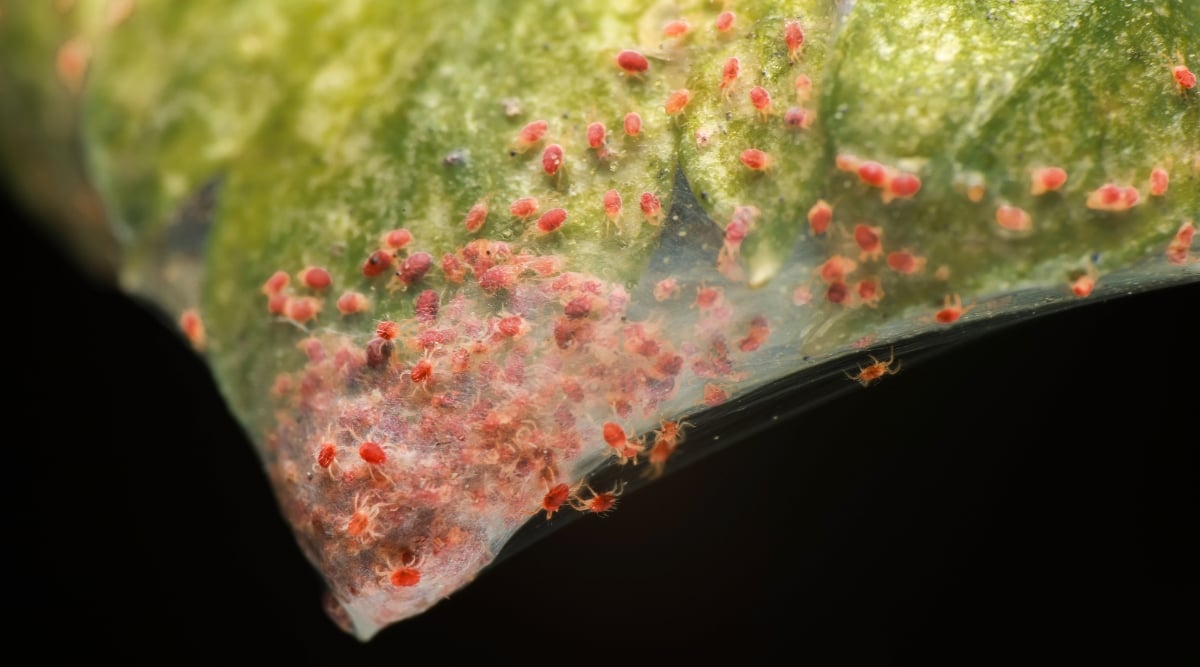
Webbing between leaves and stems signifies spider mite infestations. These sap-sucking insects can cause leaf damage, leading to yellowing or wilting. Spider mites are usually hidden under leaves and are challenging to detect until the infestation is severe.
Spider mites thrive in warm, dry environments. Maintain higher humidity levels to deter infestations and use insecticidal soap or neem oil to eliminate any visible mites effectively.
Aphids
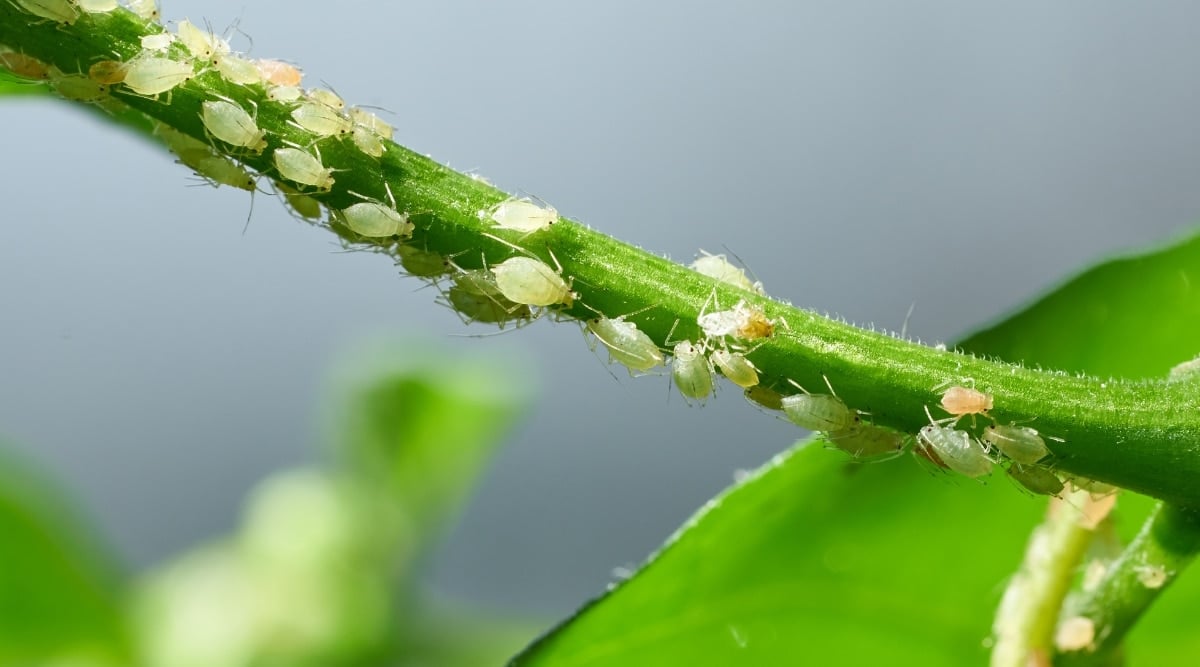

Another pest, aphids, can attack plants at any time, particularly relishing new shoots. Remove aphids by spraying them vigorously with water or applying insecticidal soap or neem oil. Replacing the top soil layer can prevent eggs from hatching and causing a new infestation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do Hoya bella flowers smell like?
Various scents can be detected from Hoya bella flowers, such as ylang-ylang, chocolate, and honey, with the most potent fragrance typically emerging at night.
Is Hoya bella slow-growing?
Hoya bella tends to grow a bit faster than other varieties. While it may take some years for young plants to flower, consider purchasing mature flowering plants for quicker results.
How do you make a Hoya bella bloom?
Encourage Hoya bella blooming through proper care, including adequate lighting and nutrients. Pruning the plant to promote bushier growth and increased flowering potential. Providing ample light is crucial for prolific flowering; consider extending exposure to daylight or investing in grow lights.
Final Thoughts
Discovering the nuances of caring for Hoya Bella can enrich your plant collection. With proper attention and care, these plants can thrive for many years. Due to their ease of propagation, they make an ideal choice for novice plant enthusiasts.






